Description
Pakistan: Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province Map
Product Details
- Title: Pakistan: Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province Map
- Publisher: Haqqi Brothers
- ISBN-13: 9789695310151 / 978-9695310151
- ISBN-10: 969531015X
- Format: Folded Map
- Language: English, Urdu
- Category: Maps & Atlases
Overview
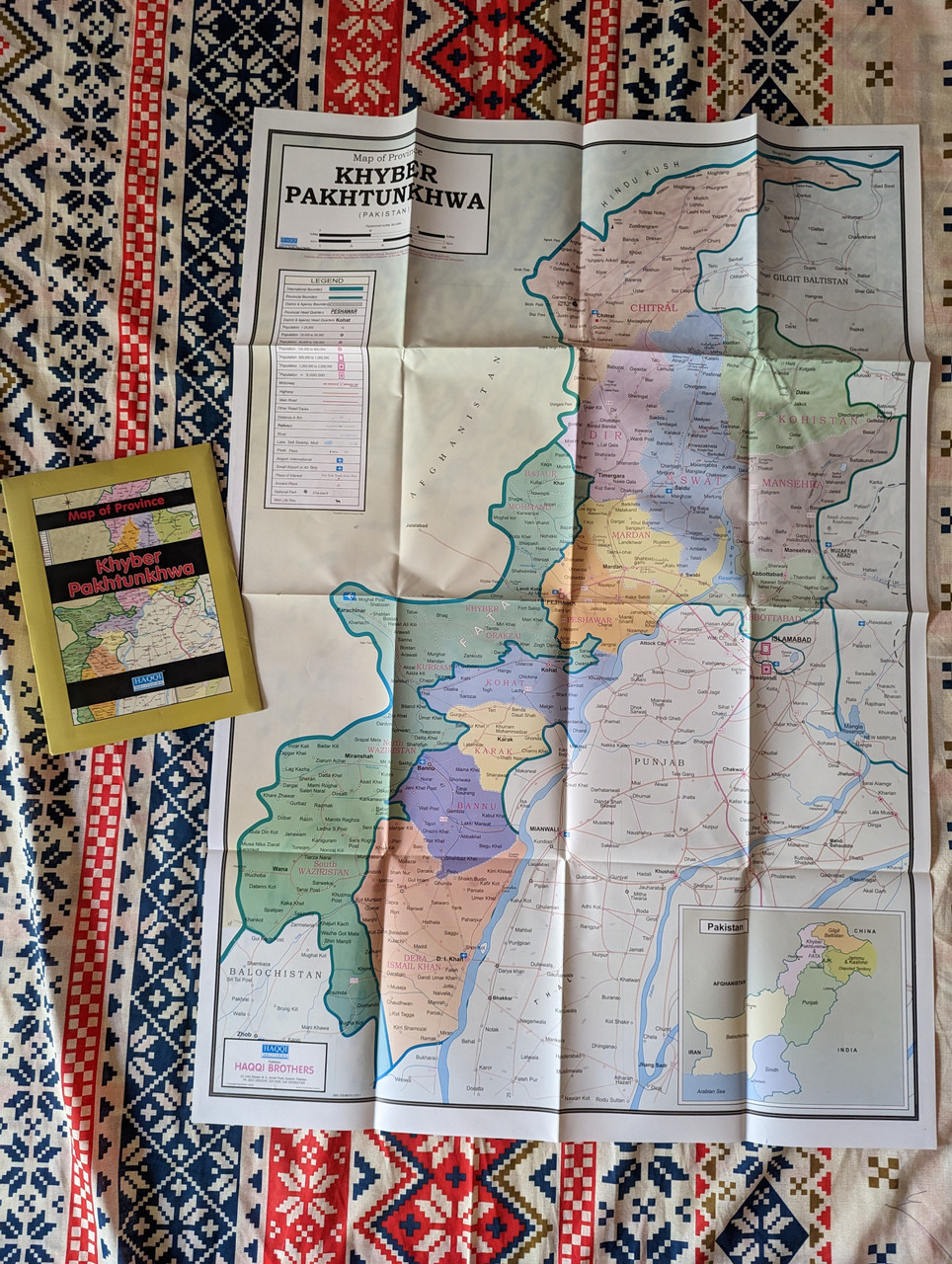
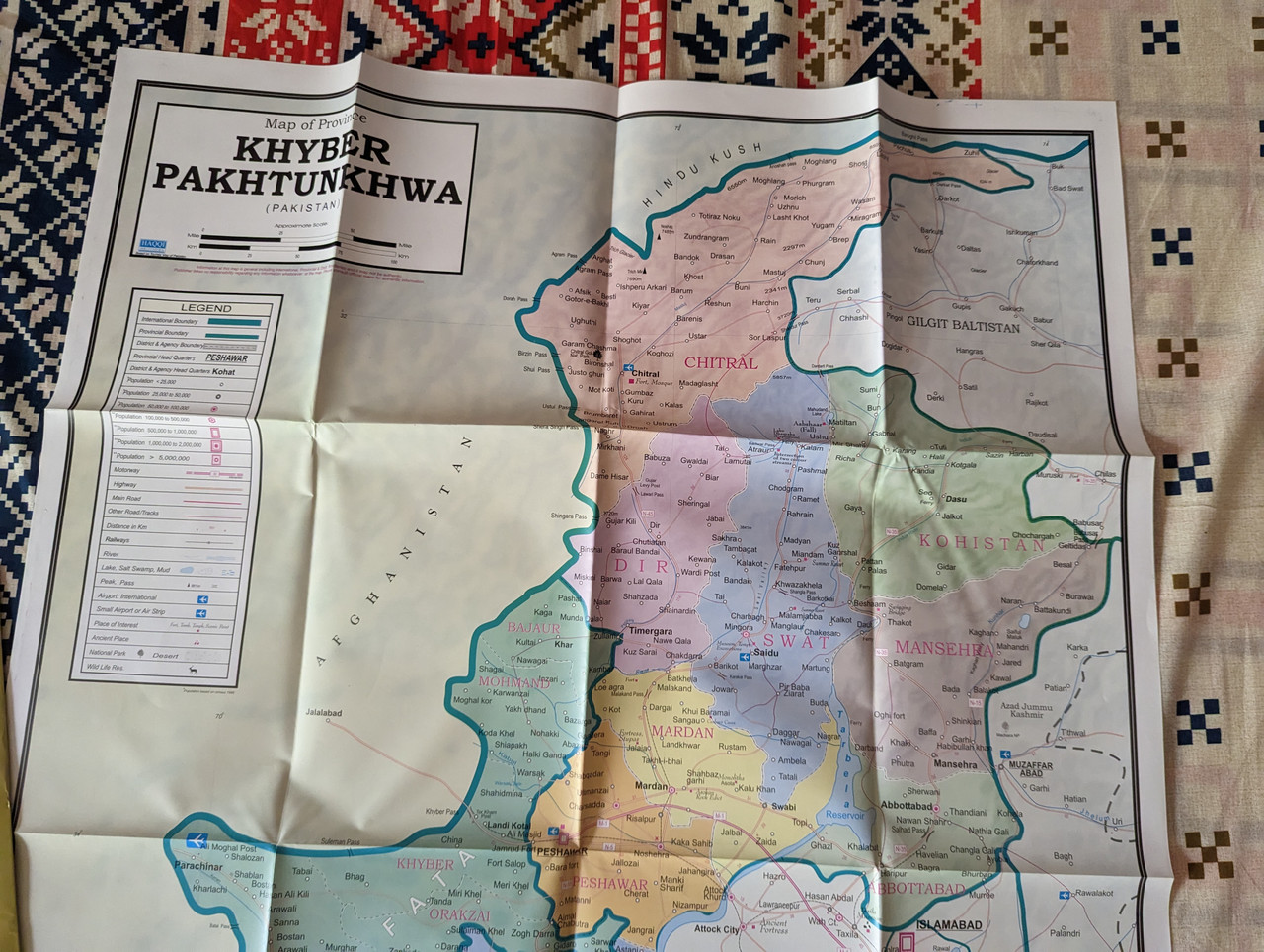
This detailed and accurate map of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP) Province is an essential resource for travelers, researchers, and geography enthusiasts. Published by Haqqi Brothers, a trusted name in cartography, this map provides a comprehensive view of the topography, road networks, cities, and landmarks within the province.
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, also known as KP or KPK, is a strategically important region in northwestern Pakistan. This map highlights the diverse terrain of KP, from its rugged mountains and valleys to its fertile plains and river systems.
Whether you are a tourist exploring historical sites, a student researching geography, or a professional needing an accurate provincial reference, this high-quality map is an excellent tool for navigation and study.
Key Features
✔ Detailed topographic representation of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa’s mountains, rivers, and valleys
✔ Clear labeling of major cities, districts, towns, and villages
✔ Highlighted road networks, highways, and key transportation routes
✔ Includes major historical, cultural, and tourist sites
✔ Bilingual labeling in English and Urdu for accessibility
✔ Printed on high-quality, durable paper for longevity
✔ Compact and foldable design for easy use and storage
Geographical Highlights of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP)
Mountain Ranges – Home to parts of the Hindu Kush, Karakoram, and Himalayas, KP features some of the most breathtaking peaks in Pakistan.
Valleys & Rivers – The Swat, Chitral, and Kaghan valleys are renowned for their natural beauty, while the Kabul and Indus Rivers run through the province.
Historic & Cultural Landmarks – From the Buddhist ruins of Takht-i-Bahi to the historic Khyber Pass, KP holds immense cultural significance.
Agricultural & Trade Hubs – Cities like Peshawar, Mardan, and Abbottabad are centers for commerce, trade, and agriculture.
Bordering Regions – KP shares its borders with Afghanistan to the west, Punjab to the southeast, Balochistan to the south, and Gilgit-Baltistan & Azad Kashmir to the north.
Who Can Benefit from This Map?
Travelers & Tourists – Ideal for exploring KP’s landscapes, historical sites, and roadways.
Students & Researchers – A valuable tool for geography and history studies.
Government & NGOs – Useful for planning development and infrastructure projects.
Hiking & Adventure Enthusiasts – Helps in planning trekking routes in mountainous regions.
Logistics & Business Professionals – Essential for understanding trade routes and urban planning.
Publisher Details
Haqqi Brothers is known for producing high-quality maps of Pakistan’s regions, providing accurate and up-to-date cartographic resources for a wide range of users.
Have you used this map? Share your experience with us in the reviews!
Hashtags
#KhyberPakhtunkhwa #PakistanMaps #HaqqiBrothers #TravelGuide #Geography #Tourism #UrbanPlanning #TopographicMaps #MountainExploration #HistoricalLandmarks
























![Sind Province Map Pakistan / Scale 1:1,000,000 [Map] by Pakistan Survey Sind Province Map Pakistan / Scale 1:1,000,000 [Map] by Pakistan Survey](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-62bdpkt7pb/images/stencil/600x600/products/2897/7056/26-M4H6-FUK3__14329.1462823316.jpg?c=2)


![Pakistan Physical Map / Scale 1:2,500,000 [Map] by Survey of Pakistan Pakistan Physical Map / Scale 1:2,500,000 [Map] by Survey of Pakistan](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-62bdpkt7pb/images/stencil/600x600/products/3171/7002/MY-8OH0-DF6D__08057.1462823315.jpg?c=2)